Introduction
Background on blockchain security issues
Blockchain has generated structured data along with inherent security qualities. In this system, the data is organized as blocks containing a bundle of transactions also each of the new blocks connects before the cryptographic chain in a way where it’s not possible to interfere. This foundation is based on decentralization, consensus where you feel secure to do the transaction. This technology will enable decentralization through the members that participate across the network. Whereas there is no failure and any user cannot change the transaction data records. However, it differs in some important security concepts.
Common security vulnerabilities
These issues are a common concern for the developers, stakeholders and project managers which will affect the blockchain system. Blockchain also contains public and private networks while the public is open to all and the private has a verified membership. To address some of the common vulnerabilities are:
- Sybil attack – Here the hacker creates different fake network nodes.
- Endpoint vulnerabilities – Here hackers study the pattern and target the device to steal the user key.
- 51% attack- When the individuals or organization collects half of the hash rate and seizes then the hackers can modify the transactions and anticipate them from being confirmed.
- Phishing attacks- Thehacker’s goal is to steal the user’s credentials.
Blockchain has many vulnerabilities but cyber security plays an important role in removing all of these problems. Also, it is better to know about vulnerabilities so that you can save the assets by preventing them.
Importance of preventing hacks and fraud
Preventing hacks and fraud in blockchain technology is important for keeping trust and security in transactions. Ensuring the honesty of the blockchain system is crucial for its adoption and constant effectiveness in many industries. Blockchain’s transparent nature can be compromised if it becomes prone to hacks or fraudulent activities. By preventing hacks and fraud, it can maintain its reputation which can build trust and a secure platform for conducting transactions and storing information.
Types of Blockchain Networks
Public Blockchains
In public blockchains, anyone can use it for free and is also allowed to participate in the free activities of the blockchain system.
Private Blockchains
In private blockchain participant users are not allowed to join directly so it requires an invitation where their information is verified.
Permissioned Blockchains
Permissioned blockchains are a combination of private and public blockchains and also allow for customization.
Permissionless Blockchains
Permissionless Blockchains also known as a public blockchain where there is no restriction and the user is not controlled by an administrator.
Common Security Risks and Attacks
51% Attack
A 51% attack is a blockchain where the malicious actors own more than 51% of a cryptocurrency’s total hashing or validating power. It owns 51% of the nodes on the network which gives the authority to alter the blockchain. In this attacker could block the user’s transaction and spend the cryptocurrency. Also, 51% of attackers that implement a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack block the network for a timeframe so that can have control of the network. It is not necessary to have 51% network power to launch an attack. Hence it can have less chance of success and the threat of a 51% attack still exists on a large blockchain like Bitcoin.
Double Spending
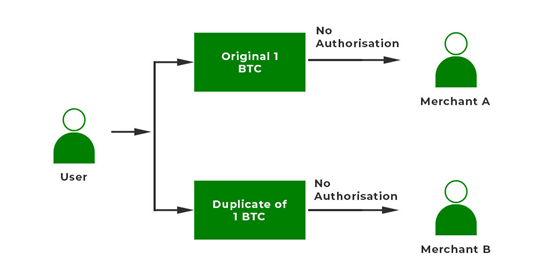
Double spending arises when the transaction of the digital currency involves the same transaction multiple times and these multiple transactions share the same broadcast on the network which can raise an issue that is unique to digital currency. There are two ways to combat double-spending clearing the counterparty and blockchain. This problem occurs when there are changes in the network that are used and are not the original ones. Preventing double-spending requires a strenuous verification process and confirms that the same input cannot be shared over multiple transactions. Example – Let’s say one user has Bitcoin and that user wants the services from merchant A and merchant B. This user wants to create multiple copies of the same Bitcoin and store the data. The user first sends the original BTC to Merchant A and gets the service also the user sends the copied version of 1 BTC to Merchant B. As the second transaction was not confirmed, the merchant accepted the bitcoin and sent the service but the cryptocurrency that was sent was invalid.
Smart Contract Bugs
A smart contract is a specialized program that is stored on the network of blockchain and is used to execute automatically of an agreement between multiple parties. There are some common bugs:
- Reentrancy attack – The most iconic exploitable smart contract which occurs when a smart contract calls for another contract in the code itself and the new call is finished and continues the execution.
- Front-running – Thesmart contracts become fully public once you submit them to the network as a pending transaction and these transactions are visible for the entire network, which allows the block miner to select the highest gas fees for the transaction.
- Simple logic error – One of the most common types of blockchain is logic errors which involve typographical errors, misinterpretation of specifications and the more serious programming errors that reduce the protection of smart contracts.
Default visibility – Default visibility is a function that states that it is public which becomes a problem when the developers do not address the visibility of the function whether it is private or it can be called within the contract
The backbone of blockchain is smart contract applications but some vulnerabilities can be exploited if not properly handled. Developers must ensure their smart contracts are secure and have no flaws.
1.1 Phishing
In this attack, there are fraud emails, text messages, calls, or fake websites designed in a way where you download the malware and share your sensitive information or personal data. So, using these tricks hackers often attack the lead information such as:- credit card fraud, ransomware attacks and data breaches which cause financial losses for the individual and the organization. The consequences of phishing include:
- Financial loss
- Data loss
- Legal proceedings
- Damage to financial history and personal reputation


It is a scam in which the attacker poses an entity or persons or different forms of communication. Hence nowadays cybercrimes have increased because it is difficult to spot phishing campaigns.
Denial of Service
A denial-of-service (DoS) is an attack which kind of cyber-attack where hackers aim to render the devices which will interrupt the functioning of the normal devices. It functions by flooding the machine with multiple requests of normal traffic which results in denial-of-service. One of the types of DoS is distributed denial-of-service which usually comes from distributed sources.
There are two methods of DoS attacks i.e., flooding services or crashing services. Flood attacks occur when the system receives traffic due to which its buffer also slows down. The most popular flood attacks are:
- Buffer overflow attacks
- ICMP flood
- SYN flood
The damage in the service of the DoS attack can be fixed in a short time by the implementation of a firewall with allow or deny rules. However, there is a type of DoS attack that is not so easy to detect.
Analysis of New Security Protocols
Consensus mechanism improvements
A consensus mechanism is a program that is used in blockchain to achieve distributed agreement and it is implemented in a network with some processes and users. For most of the cryptocurrencies, blockchain uses this for verification and audits. There are multiple improvements to enhance security, efficiency and some of these improvements are:
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
- Proof of Authority (PoA)
- Hybrid Consensus Mechanisms
These mechanisms are widely useful as distributed ledger networks and platforms that have been generated for business will allow entities to select from the module according to their needs which has support of consensus mechanisms. Hence improving the consensus mechanism which is important for the growth of blockchain and these approaches such as proof of stake aim to build blockchain faster and more sustainable.


Proof-of-Stake protocols to replace energy-intensive Proof-of-Work
Proof of stake is a consensus mechanism that ensures only the validated user gets added to the blocks for the transactions and also has a validator’s locker where cryptocurrency is stored to secure the network. The community of Ethereum is working to change similar to Ether currency which has been generated to reduce the carbon footprint of blockchain and this method is known as Proof of Stake (PoS).
Proof of stake in Ethereum 2.0 has a target to achieve the outcome same as proof of work which is to secure the verification in the blockchain for the transaction. Proof of stake has several advantages:
- In this you do not require a fancy computer because there is no high computing power.
- It has lower hardware requirements which use less energy.
- Most individuals participate in the Ethereum node, which enables decentralization.
Hence Ethereum 2.0 aims to show the transition from PoW to PoS which will also introduce sharding and many more improvements. The community believes in Proof-of-Stake as a solution that will address scalability concerns by increasing transaction capacity and reducing gas fees associated with transactions. Polkadot is a muti-chain network that allows for different blockchains to transfer messages and also enables the decentralized web in which users are in control. However, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) protocols are gaining attention to replace the energy-intensive consensus mechanisms like the one used in Polkadot, which is based on Proof-of-Work (PoW).[1]
- Encryption and hashing advancements – Using secure encryption to protect private keys
The private keys are also known as secret keys which are variable in cryptography and are used with algorithms to read and store the data. To secure the encrypted private key, robust algorithms such as advanced encryption standards and store the keys in a safe location. Also, by adding a passphrase to encrypt the key and keeping the passphrase separate from the encrypted key.
Even though hackers want to gain access to the private key they will need a password and decrypt the private key which allows the owner time to identify and eliminate the issue. Technical examples are SNARKs and STARKs have zero knowledge-proof technology allowing one party to prove to another that the statement is true without any leak of information.
- Multi-layered authentication – Combining public or private keys
This combining of the public or private keys with biometric and two-factor authentication provides a strong and multi-level method toward security. This is also helpful in the case of biometric data which provides fingerprint or face recognition same as two-factor authentication which is more important and makes it difficult for unauthorized access to occur.
One of the examples is multisig which is also known as multisignature which is a requirement for transaction. It offers a balance of resilience and security in the case of digital assets such as Bitcoin. It will also ensure that it makes it tougher for someone to steal your assets. It also provides a paradigm that helps to design multsigs that address topics like a single point of failure, separation of interests, separation of duties and many more.
Impact on Blockchain Adoption
Increased trust and confidence in blockchain security
Blockchain is not a trusted technology but it is more about confidence, it will increase confidence in the terms of the operation of computational systems. Mostly depends on the underlying governance structure and this requires trusting a disturbed web of actors. There are theories like constitutional and polycentric which can help to improve blockchain governance.
By this technique, blockchain can secure the digital signatures and timestamping which makes it difficult for a person who tries a malicious activity who try to manipulate or steal the digital assets. This increases the trust and confidence among the users in the ecosystem of the multiverse.
Facilitation of blockchain integration across industries
Block integration has been facilitated across all industries which includes the identification of cases that involve blockchain technology that can add some value by generating regulatory frameworks that will support blockchain adoption. It also provides training, education and collaboration of multiple stakeholders and privacy concerns which are important factors that have shown success for blockchain integration.
The integration of blockchain technology has shown its potential for revolution in the form of digital and slowly it is increasing innovation not only in the finance sectors but also in healthcare, supply chain management, the energy sector and real estate. Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies will have a dynamic and developing future with innovations.
Continued decentralization of blockchain networks
In blockchain, decentralization means to transfer of control and making decisions from a centralized entity which have the authority to disturber network and it reduces the steps of trust that users must place in one another which will also degrade the functionality of the network. There are some beneficial factors of decentralization:
- Provides a trustless environment
- Reduces points of weakness
- Improves data reconciliation
- Optimizes resource distribution
The continued decentralization of blockchain networks is important for long-term security, resilience, and trustworthiness and more nodes will join the network and contribute to consensus, the system becomes more resistant to attacks and censorship.
Impact of Attacks
Financial Losses
“While the blockchain system represents advances in encryption and security, it is vulnerable in some of the same ways as other technology, as well as having new vulnerabilities unique to blockchain,” Madnick says.
These attacks can result in more financial losses on the blockchain network that not only target the entities but the whole trust built by the technology. These cases can lead to a reduction of confidence of investors, market volatility and an increase of scrutiny.
Also, it is interconnected with the old financial system also means that an attack can show more effect on the whole market including the regulatory environments, necessitating robust security measures. In conclusion, attacks on blockchain networks can lead to significant financial losses, impacting both individual entities and the broader economy.
Reputation Damage
- Attacks on blockchain networks can result in reputation damage.
- Compromised networks can lead to a loss of trust from users, investors, and the public.
- Reputation damage can impact the authority and perceived reliability of the blockchain platform.
- Long-term implications for adoption and usage make reputation damage a critical concern for blockchain security.
These attacks on blockchain networks can have more consequences in terms of reputation damage which will mostly show as risks and not safe for the integration of the ecosystem.
Erosion of Trust
- Security breaches can lead to the erosion of trust in blockchain networks.
- Users and stakeholders will lose confidence in the network’s ability to safeguard their assets and data.
- Erosion of trust can delay the widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
- Preserving trust is crucial for the continued advancement of blockchain networks.
Erosion of Trust will result in a delay in the adoption of blockchain and technology advancement so to maintain trust among the user and stakeholders is necessary to build a more robust blockchain ecosystem.
Security Frameworks and Models
IBM Blockchain Security Model
IBM Blockchain Security Model is an inclusive approach that protects the network of blockchain and its application which also includes security measures, including encryption, identity management and consensus protocols that secure the integrity and privacy of data.
IBM’s model gives more importance to regular monitoring and rapid incident response to address emerging security challenges by this combination of these elements it aims to provide resilience and trust for the blockchain ecosystem which is implemented all over the industries.
It provides a security framework that addresses the challenges of blockchain technology and this model highlights its commitment the trust and reliability in blockchain implementations across various sectors.
Chainalysis On-Chain Security
Chainalysis is a renounced company that provides security and intelligence solutions for the blockchain ecosystem and they use blockchain to identify malicious activity, trace funds and some other regulations. Some of the tools for cryptocurrency compliance provided by Chain analysis include:
- Chainalysis Sanctions API
- Chainalysis Sanctions Screening oracle
- Chainalysis KYT
Hence, Chainalysis provides insights into transactional patterns, illicit activities, and compliance measures and also contributes to the overall security and integrity of blockchain networks. This information helps to increase trust and compliance within the blockchain ecosystem.
Emerging Security Trends
Quantum computing resistant encryption
- Quantum computing-resistant encryption means cryptographic algorithms that are designed to survive attacks from quantum computers.
- These methods aim to address the potential threat quantum computers pose to traditional cryptographic systems that could become weak to quantum-based attacks.
- Quantum-resistant encryption algorithms are being developed to allow the long-term security of private data in the aspect of advancing quantum computing capabilities.
- The main aim of encryption techniques is that they can effectively protect data even in a future where quantum computers may pose an important risk to current encryption standards
Its goal is to mitigate the risks with the help of quantum computers to traditional cryptographic systems which will protect the data from attack and provide long-term security
Blockchain integration with trusted hardware
- Blockchain integration with trusted hardware is a combination of blockchain technology with secure hardware components like trusted execution environments.
- This integration will enhance the security and privacy of blockchain networks which will provide a secure environment for executing sensitive operations and storing the cryptocurrency keys.
- Trusted hardware allows features such as confidential transactions and secure identity management against various forms of attacks for the security of blockchain systems.
- This integration has the potential to show the security and privacy concerns which makes blockchain more suitable for sensitive applications.
By allowing these features such as confidential transactions and secure identity management, this integration will expand the applicability of blockchain technology to sensitive use cases.
Decentralized storage and file sharing
- Decentralized file sharing allows data to be distributed and accessed without reliance on a centralized server or any interconnected nodes.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) technology is commonly used to ease the storage and sharing of files across the network, promoting a distributed approach to data management.
- In this model, network users store their resources and collectively form a decentralized infrastructure for file sharing and access.
- The decentralized nature of this method offers benefits such as increased resilience and it will also have likely for improved scalability and efficiency in data distribution.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Blockchain technology has also some vulnerabilities such as Sybil attacks and phishing that affect public, private, permissioned, and permissionless blockchains some risks i.e., 51% attacks and smart contracts which require some security. There is a consensus mechanism that has shown advanced improvement, two-step authentication which increases the protection which also includes the major shift of Ethereum 2.0 and Polkadot towards proof-stake protocols. IBM Blockchain Security Model and Chainalysis On-Chain Security provide robust frameworks to address these challenges.
We recommend cybersecurity for education, multi-layered authentication adoption, regular security audits, Regular Security Audits, Stay Informed on Emerging Security Protocols, Quantum-Resistant Encryption, exploring decentralized Storage Solutions and industry collaboration and by this implementation it will measure its security and widespread adoption for the blockchain ecosystem across the industries.












You must be logged in to post a comment.